Database of frameworks¶
This notebook can be downloaded here.
There are several predefined frameworks in pyrigi.frameworkDB.
import pyrigi.frameworkDB as frameworks
Complete frameworks¶
Complete() returns \(d\)-dimensional complete frameworks.
frameworks.Complete(2)
Framework(Graph.from_vertices_and_edges([0, 1], [(0, 1)]), {0: ['0', '0'], 1: ['1', '0']})
frameworks.Complete(3, dim=1)
Framework(Graph.from_vertices_and_edges([0, 1, 2], [(0, 1), (0, 2), (1, 2)]), {0: ['0'], 1: ['1'], 2: ['2']})
frameworks.Complete(4, dim=3)
Framework(Graph.from_vertices_and_edges([0, 1, 2, 3], [(0, 1), (0, 2), (0, 3), (1, 2), (1, 3), (2, 3)]), {0: ['0', '0', '0'], 1: ['1', '0', '0'], 2: ['0', '1', '0'], 3: ['0', '0', '1']})
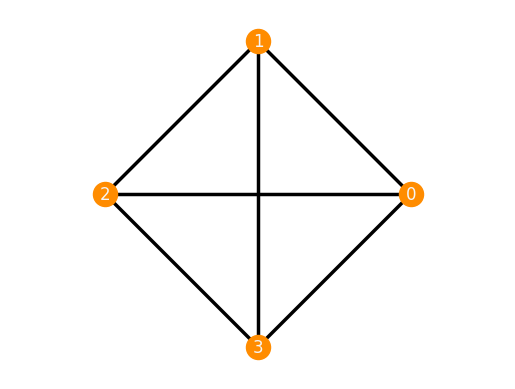
K4 = frameworks.Complete(4, dim=2)
print(K4)
K4.plot()
Framework in 2-dimensional space consisting of:
Graph with vertices [0, 1, 2, 3] and edges [[0, 1], [0, 2], [0, 3], [1, 2], [1, 3], [2, 3]]
Realization {0:(1, 0), 1:(0, 1), 2:(-1, 0), 3:(0, -1)}
Currently, for \(d\geq 3\), the number of vertices must be at most \(d+1\) so the graph can be realized as a simplex.
try:
frameworks.Complete(5, dim=3)
except ValueError as error:
print(error)
The number of vertices n has to be at most d+1, or d must be 1 or 2 (now (d, n) = (3, 5).
Complete bipartite frameworks¶
CompleteBipartite() returns 2-dimensional complete bipartite frameworks.
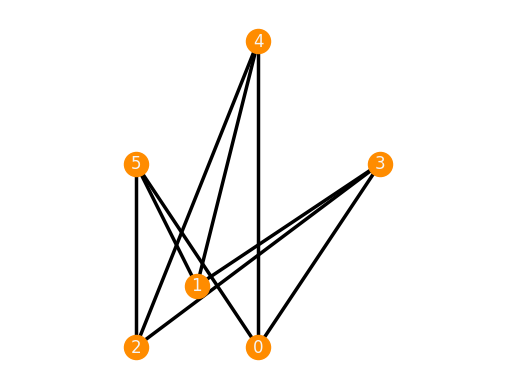
K33 = frameworks.CompleteBipartite(3, 3)
K33.plot()
K33.is_inf_rigid()
True
The first construction of a flexible realization by Dixon places one part on the \(x\)-axis and the other part on the \(y\)-axis.
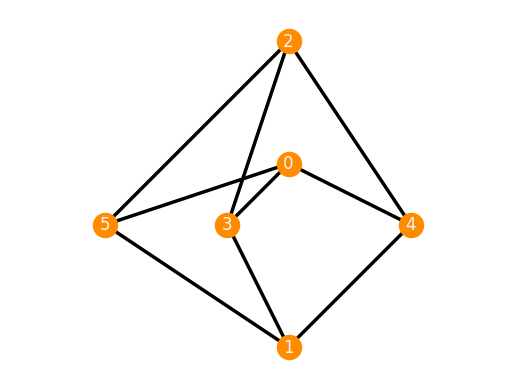
K33_dixonI = frameworks.CompleteBipartite(3, 3, 'dixonI')
K33_dixonI.plot()
K33_dixonI.is_inf_flexible()
True
Cycle frameworks¶
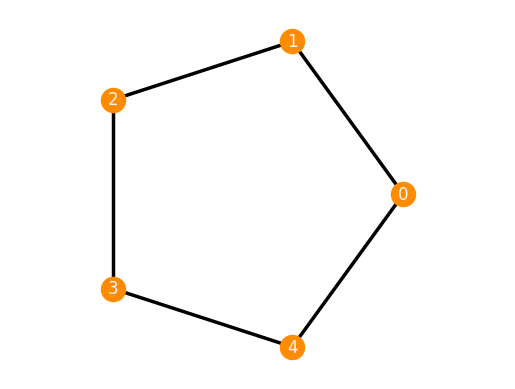
Cycle() returns \(d\)-dimensional frameworks on cycle graphs.
The restriction on the number of vertices w.r.t. the dimension is the same as for complete frameworks.
C5 = frameworks.Cycle(5)
print(C5)
C5.plot()
Framework in 2-dimensional space consisting of:
Graph with vertices [0, 1, 2, 3, 4] and edges [[0, 1], [0, 4], [1, 2], [2, 3], [3, 4]]
Realization {0:(1, 0), 1:(-1/4 + sqrt(5)/4, sqrt(sqrt(5)/8 + 5/8)), 2:(-sqrt(5)/4 - 1/4, sqrt(5/8 - sqrt(5)/8)), 3:(-sqrt(5)/4 - 1/4, -sqrt(5/8 - sqrt(5)/8)), 4:(-1/4 + sqrt(5)/4, -sqrt(sqrt(5)/8 + 5/8))}
frameworks.Cycle(5, dim=1)
Framework(Graph.from_vertices_and_edges([0, 1, 2, 3, 4], [(0, 1), (0, 4), (1, 2), (2, 3), (3, 4)]), {0: ['0'], 1: ['1'], 2: ['2'], 3: ['3'], 4: ['4']})
frameworks.Cycle(5, dim=4)
Framework(Graph.from_vertices_and_edges([0, 1, 2, 3, 4], [(0, 1), (0, 4), (1, 2), (2, 3), (3, 4)]), {0: ['0', '0', '0', '0'], 1: ['1', '0', '0', '0'], 2: ['0', '1', '0', '0'], 3: ['0', '0', '1', '0'], 4: ['0', '0', '0', '1']})
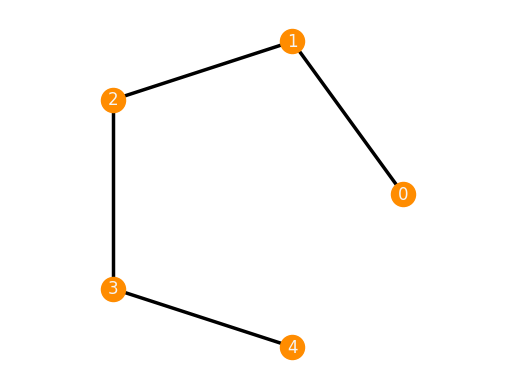
Path frameworks¶
Path() returns \(d\)-dimensional frameworks on path graphs.
The restriction on the number of vertices w.r.t. the dimension is the same as for complete frameworks.
P5 = frameworks.Path(5)
print(P5)
P5.plot()
Framework in 2-dimensional space consisting of:
Graph with vertices [0, 1, 2, 3, 4] and edges [[0, 1], [1, 2], [2, 3], [3, 4]]
Realization {0:(1, 0), 1:(-1/4 + sqrt(5)/4, sqrt(sqrt(5)/8 + 5/8)), 2:(-sqrt(5)/4 - 1/4, sqrt(5/8 - sqrt(5)/8)), 3:(-sqrt(5)/4 - 1/4, -sqrt(5/8 - sqrt(5)/8)), 4:(-1/4 + sqrt(5)/4, -sqrt(sqrt(5)/8 + 5/8))}
frameworks.Path(5, dim=1)
Framework(Graph.from_vertices_and_edges([0, 1, 2, 3, 4], [(0, 1), (1, 2), (2, 3), (3, 4)]), {0: ['0'], 1: ['1'], 2: ['2'], 3: ['3'], 4: ['4']})
frameworks.Path(5, dim=4)
Framework(Graph.from_vertices_and_edges([0, 1, 2, 3, 4], [(0, 1), (1, 2), (2, 3), (3, 4)]), {0: ['0', '0', '0', '0'], 1: ['1', '0', '0', '0'], 2: ['0', '1', '0', '0'], 3: ['0', '0', '1', '0'], 4: ['0', '0', '0', '1']})
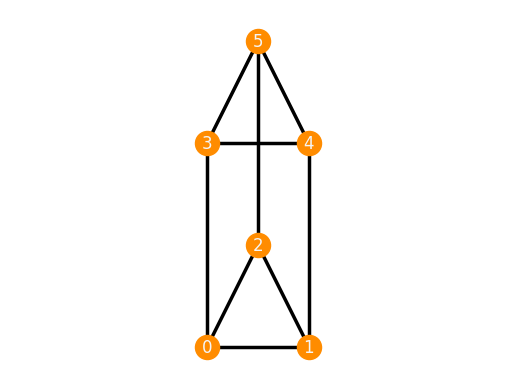
3-prism¶
A general realization of 3-prism.
TP = frameworks.ThreePrism()
TP.plot()
TP.is_inf_rigid()
True
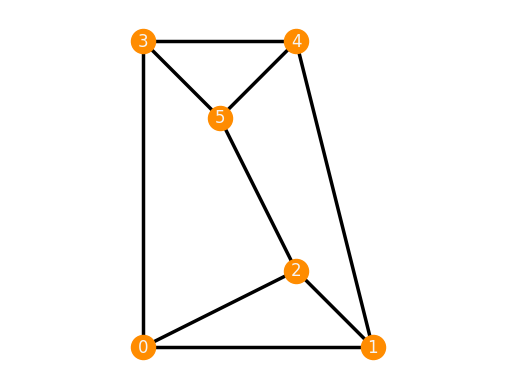
Infinitesimally flexible, but continuously rigid realization.
TP = frameworks.ThreePrism('parallel')
TP.plot()
TP.is_inf_rigid()
False
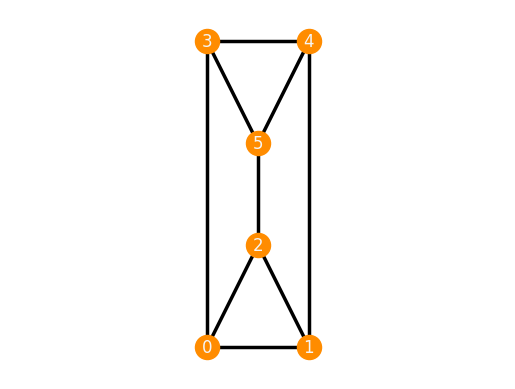
Continuously flexible realization.
TP = frameworks.ThreePrism('flexible')
TP.plot()
TP.is_inf_rigid()
False
Further frameworks¶
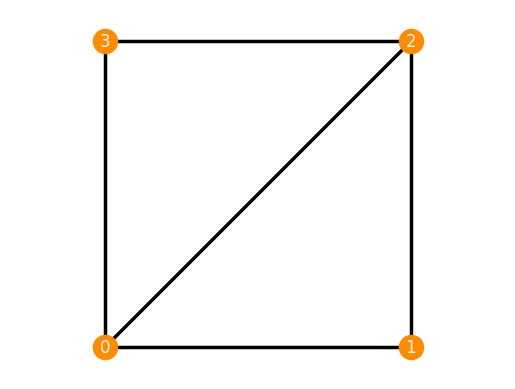
Diamond = frameworks.Diamond()
print(Diamond)
Diamond.plot()
Framework in 2-dimensional space consisting of:
Graph with vertices [0, 1, 2, 3] and edges [[0, 1], [0, 2], [0, 3], [1, 2], [2, 3]]
Realization {0:(0, 0), 1:(1, 0), 2:(1, 1), 3:(0, 1)}
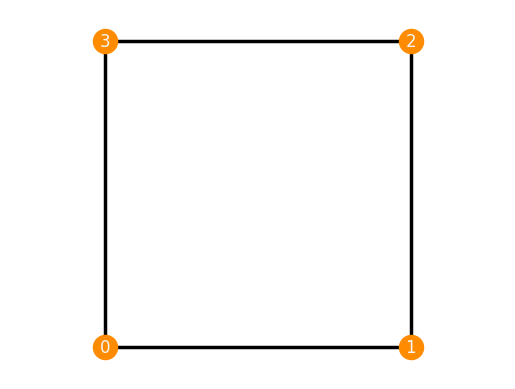
Square = frameworks.Square()
print(Square)
Square.plot()
Framework in 2-dimensional space consisting of:
Graph with vertices [0, 1, 2, 3] and edges [[0, 1], [0, 3], [1, 2], [2, 3]]
Realization {0:(0, 0), 1:(1, 0), 2:(1, 1), 3:(0, 1)}
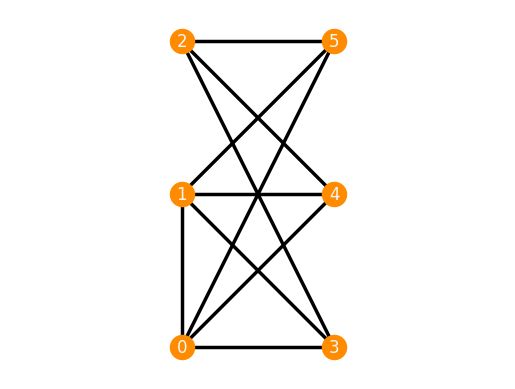
frameworks.K33plusEdge().plot()
frameworks.ThreePrismPlusEdge().plot()
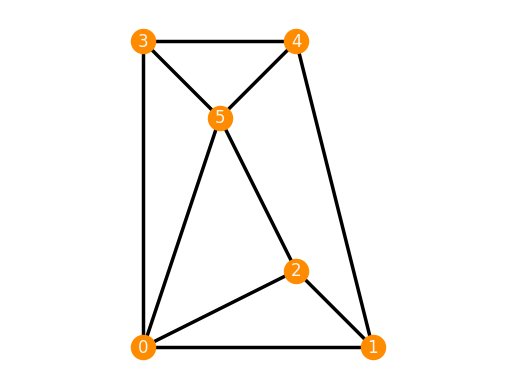
frameworks.Frustum(3).plot()
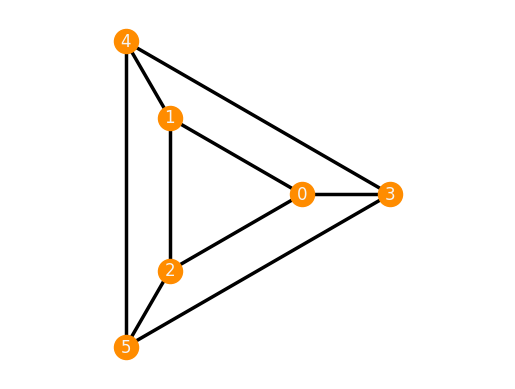
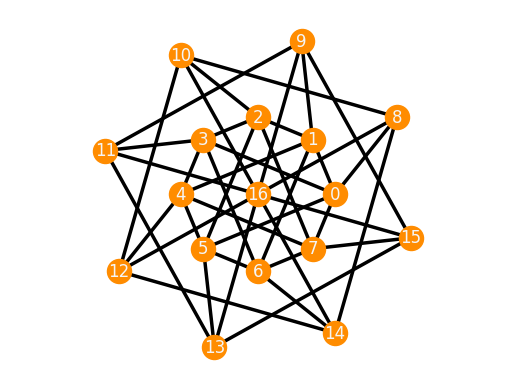
frameworks.CnSymmetricFourRegular(10).plot()
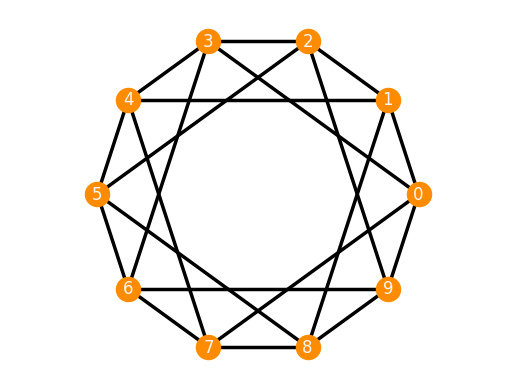
frameworks.CnSymmetricWithFixedVertex(8).plot()